To improve air quality, Connecticut’s Dept. of Energy and Environmental Protection says the state has seven years to reduce transportation and building emissions by 30%. Emissions testing in CT is a big part of these concerted efforts, so drivers residing in the Constitution State must get their vehicles to an emissions testing facility every two years, unless the vehicle is 4 years old or newer. For now, in 2022, those with vehicle models from 2018 to 2021 don’t need to undergo and pass an emissions inspection.
Use eTags© to Quickly Complete Your DMV Service. Renewals, Title Transfers and More, All Online!
If you don’t get regular emissions testing, the Connecticut DMV will block your registration renewal just like it would for unpaid property taxes, parking ticket, or lack of car insurance. So it’s important to follow through, because no registration means no driving allowed.
The CT DMV sends out notices for emissions inspections at least 45 days before testing is due
Connecticut emissions testing types
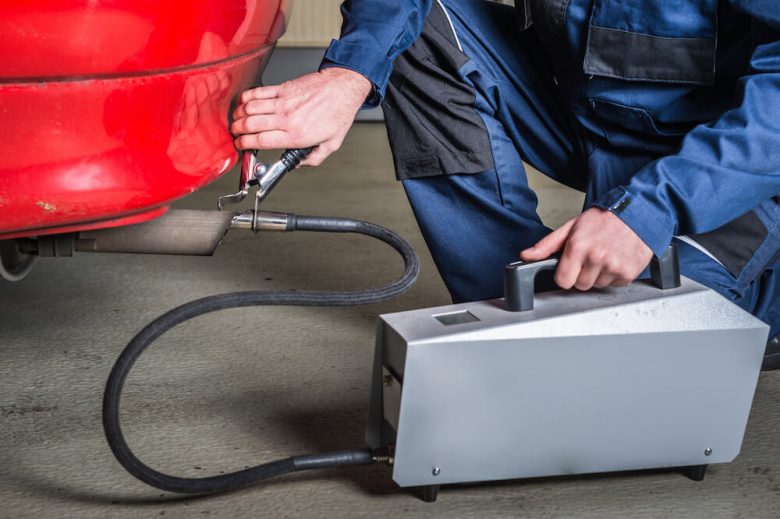
The Connecticut Emissions Program helps find malfunctioning pollution control devices and when fuel is wasted. The inspection your vehicle is subjected to depends on your vehicle’s make, model year, fuel, and driveline.
An on-board diagnostic test (OBD)
If your car is model year 1996 or newer, you can get an OBD test. If your truck, van or SUV has a gross weight of 8,501-10,000 pounds, you must also get an on-board diagnostic on 2008 model year and 2007 diesel-powered ones. If you have a 1997 and newer diesel-powered vehicle, you also need an OBD.

The on-board diagnostic test verifies emissions while vehicle is operating, since most 1996 model year cars and newer have electronic sensors of engines and emissions control system. If your check engine light stays on while car is tested, the vehicle will automatically fail. You could have a problem with the engine, transmission or emissions control. Thanks to a communication cable from testing equipment to your vehicles, the info is retrieved so nothing is installed to perform the OBD test.
All vehicles are subject to catalytic converter visual test no matter the emissions test
A pre-conditioned two-speed idle test (PCTSI)
This Connecticut emissions test is for 2007 vehicles and older with gross weight between 8,501-10,000 pounds. The pre-conditioned two-speed idle test measures tailpipe emissions (hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide) at both cruise and idle speed.
If you get this sort of emissions test, your vehicle must undergo a gas cap pressure leak test. This ensures the gas tank is properly sealed so the car’s evaporative emission system correctly disposes of fuel vapors.
A modified snap acceleration test (MSA)
If you have a diesel vehicle that’s 2006 or older with gross weight between 8,501-10,000 pounds, an MSA test will measure the density of tailpipe smoke from the vehicle. Also, all 1996 diesel vehicles heavier than 10,000 pounds must undergo the modified snap acceleration test.
Connecticut conducts emissions tests for about 1.3 million vehicles every year

Failed Connecticut emissions test: now what
If your car didn’t pass the CT emissions test, you must repair and retest within 60 days from the first inspection. A failed emissions test means your vehicle surpasses the allowable emissions for the model year. You can repair anywhere or even do it yourself if you know your way around cars.
The Connecticut DMV though recommends you repair your car at a certified emissions repair facility also known as CERF since they’re trained in emissions-related failed inspections. Visiting a CERF may also help you qualify for a cost waiver if the car fails a second test.
SEE ALSO: CONNECTICUT REGISTRATION RENEWAL-RENEW CT LICENSE PLATES ONLINE








